Blog
Exploring the frontiers of AI, language models, and multilingual technology
CoSHE-Eval: A Code-Switching ASR Benchmark for Hindi–English Speech
CoSHE-Eval is a 30-hour Hindi–English code-switching evaluation dataset designed to benchmark ASR systems under realistic multilingual speech conditions. Built using a hybrid pipeline of Gemini-based bilingual transcription and human verification, it captures natural Hinglish mixing and emotional tone tags.
Read more →Dhrith: Emotionally Intelligent ASR for India’s Multilingual Voices
Dhrith is our next-generation ASR model that listens beyond words. It understands emotion, rhythm, and code-switched language — capturing not just what is said, but how it's said. Built for India's multilingual reality, Dhrith brings emotional intelligence to speech recognition.
Read more →
Introducing Pragna-1B: Soket AI Labs' Multilingual Language Model for Indian Languages
We at Soket AI Labs are thrilled to unveil India's first open source multilingual model, Pragna-1B available in four Indian languages - Hindi, Gujarati, Bangla and English. The model is designed to cater to the rich tapestry of Indian languages, significantly expanding the horizons of AI inclusivity and accessibility.
Read more →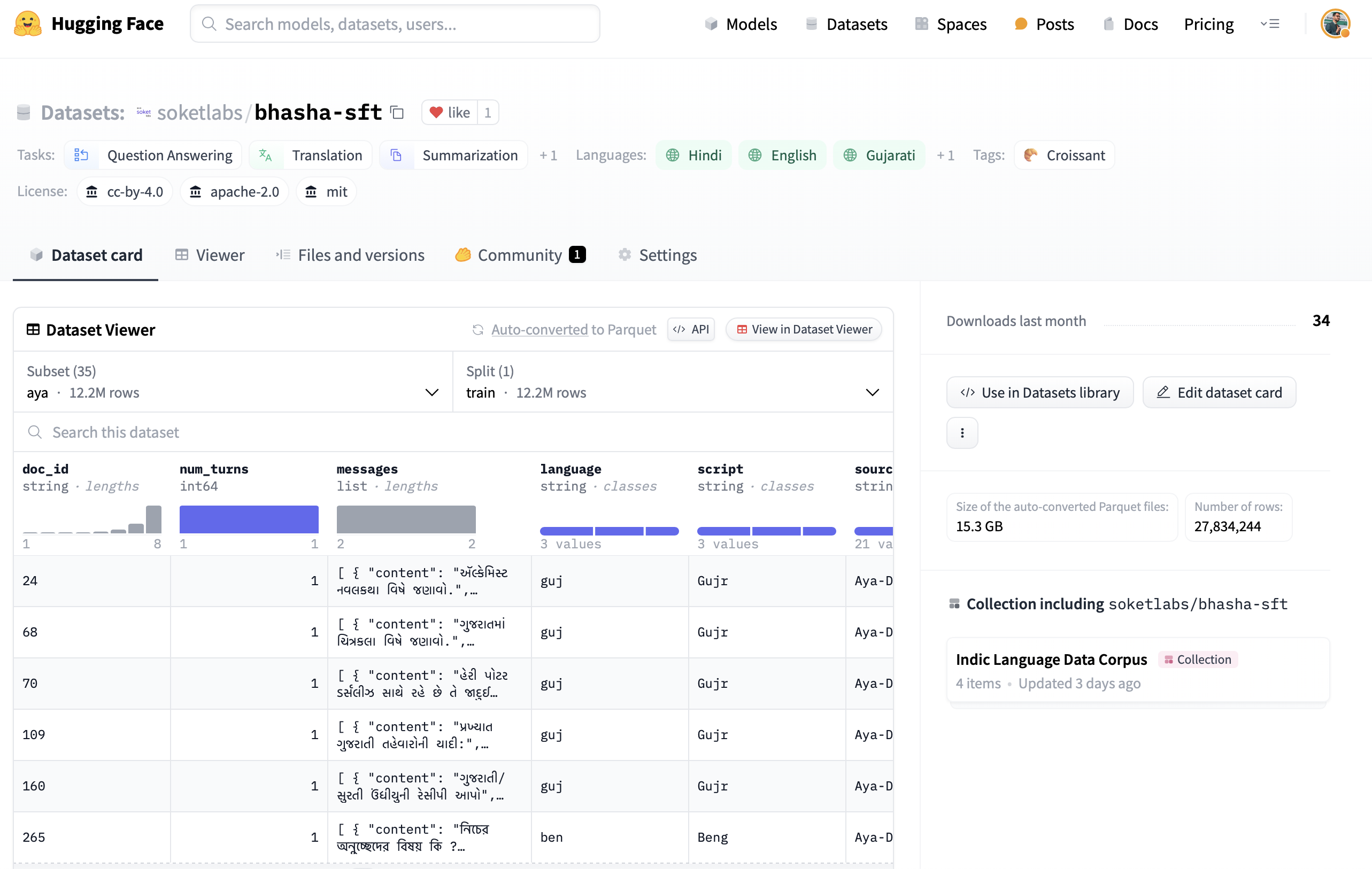
Availability of the Bhasha SFT Dataset for Supervised Fine-Tuning of Indic Language Models
We are pleased to inform the NLP community about the availability of the Bhasha SFT dataset, an extensive collection curated by Soket AI Labs for the supervised fine-tuning of Multilingual Large Language Models (LLMs), focusing on Indic languages. The dataset features over 13 million instruction-response pairs in four languages: Hindi, Gujarati, Bengali, and English.
Read more →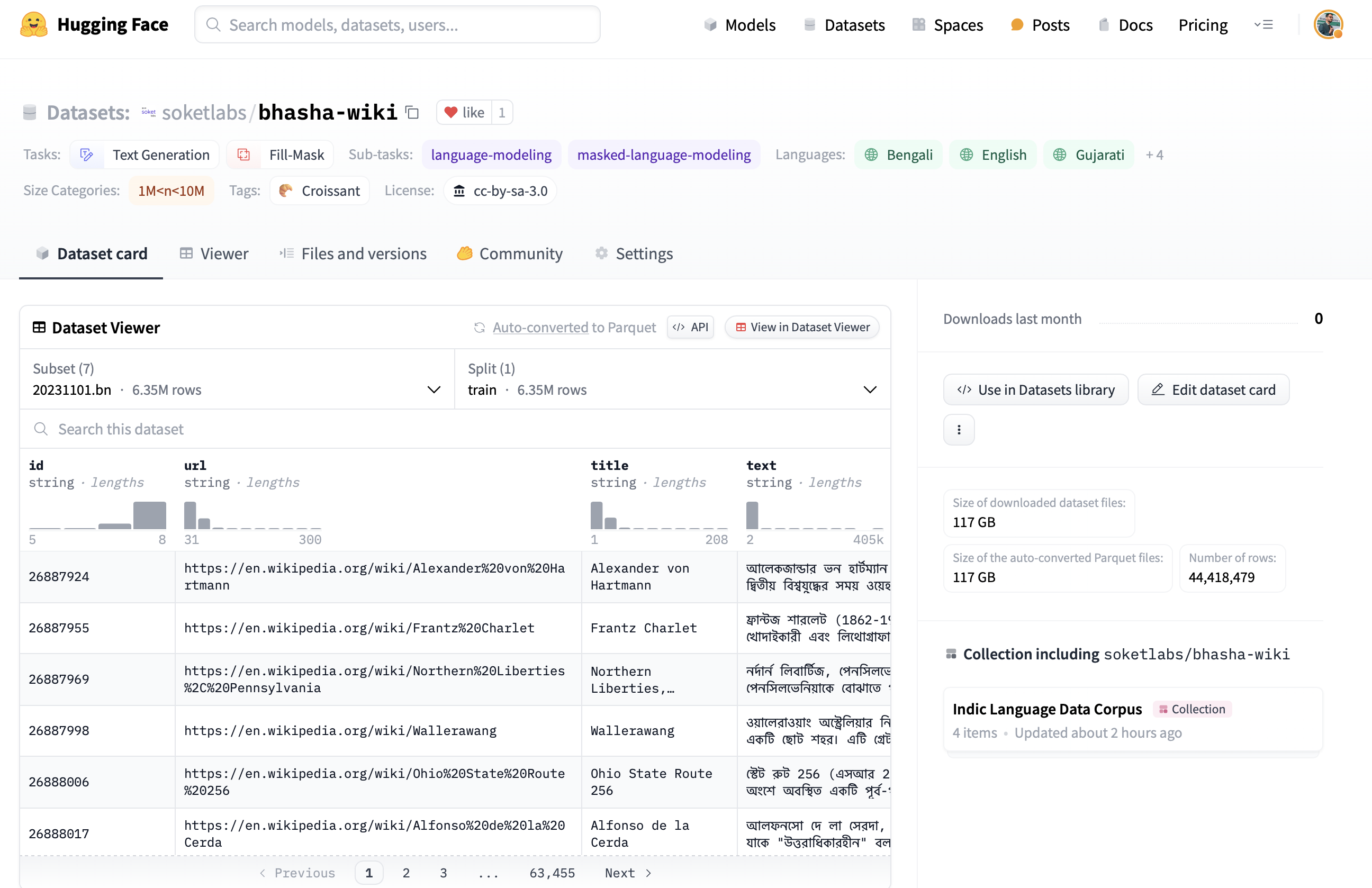
Introducing the "Bhasha" Series: Advancements in Indic Language AI Datasets
Soket Labs is pleased to announce the release of the "Bhasha" series, commencing with two significant datasets: "bhasha-wiki" and "bhasha-wiki-indic". These datasets are engineered to support the development of AI models that are attuned to the linguistic and cultural nuances of India, representing a crucial step forward in the diversification of linguistic resources in computational linguistics.
Read more →